Table of Contents
What is Penetration Test?
Penetration Testing, also known as “Sızma Testi” in Turkish, is the process of testing a computer system, network, and applications to identify and prevent security vulnerabilities from being exploited by malicious individuals. Penetration testing is a form of ethical hacking conducted to assess the security level of an organization’s or company’s IT infrastructure.
The goal of penetration testing is to identify weaknesses and security flaws in systems using the same methods that attackers might use. This process can cover different areas, such as network security, operating system security, and physical security. Understanding the attack and defense strategies and identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities are essential aspects of penetration testing.
Penetration tests are usually planned and organized to target specific systems. Tests can be conducted using both automated tools and manual methods. After identifying weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and security flaws in the system, a report is generated and presented to the organization or company. This report includes the identified security issues, their potential impacts, and recommended solutions.
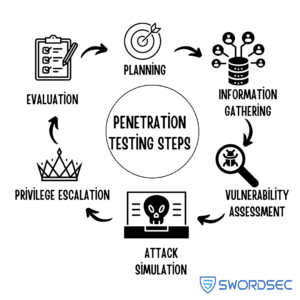
Steps involved in a Penetration Test:
- Planning and Target Identification: Determine which systems will be tested, the duration of the penetration test, and the methods to be used.
- Information Gathering: Gather as much information as possible about the target system or application, including network topology, server configurations, software in use, users and their permissions, access points, and other critical details. This information is used to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Detection: After gathering information, automated tools and manual techniques are used to detect security vulnerabilities in the target system or application. This can involve using network scanners, vulnerability scanning tools, and specialized software to check for weaknesses in areas such as network security, web application security, and operating system security.
- Attack Simulation: Once vulnerabilities are identified, simulated attacks are performed using the detected security flaws. These attacks may include port scanning, brute-force attacks, phishing attempts, firewall evasion, and other techniques. It is important to ensure that the test is conducted in a controlled environment, not in the production environment.
- Access Attempts and Privilege Escalation: During the penetration test, attempts are made to gain access to the target systems or applications and to escalate privileges. This can be done by detecting weak passwords, exploiting vulnerabilities, or deceiving other authorization mechanisms.
- Evaluation and Reporting: After the penetration test is complete, the results are evaluated, and a report is generated. The report includes details of the findings, the potential impacts of the identified security issues, and suggested solutions.
Common Penetration Testing Tools:
- Nmap: Used as a network scanner to detect devices and open ports in the target network.
- Metasploit: A penetration testing framework used to attack computer systems and exploit security vulnerabilities.
- Burp Suite: A penetration testing tool for web applications, used to detect security vulnerabilities, automate security tests, and simulate attack scenarios.
- Wireshark: An analysis tool used to capture and analyze network traffic for security and vulnerability detection purposes.
- Nessus: A vulnerability scanning tool used to detect security flaws in network systems and applications.
- Nikto: An open-source penetration testing tool targeting web servers to automatically scan for potential security vulnerabilities.
- sqlMap: A tool used to detect SQL injection attacks and exploit security vulnerabilities in database systems.
In conclusion, penetration testing is a crucial step to detect and mitigate security vulnerabilities in web and mobile applications, computer systems, and networks. Conducting regular penetration tests and implementing the necessary security measures based on the results can significantly enhance an organization’s resilience against potential cyberattacks.